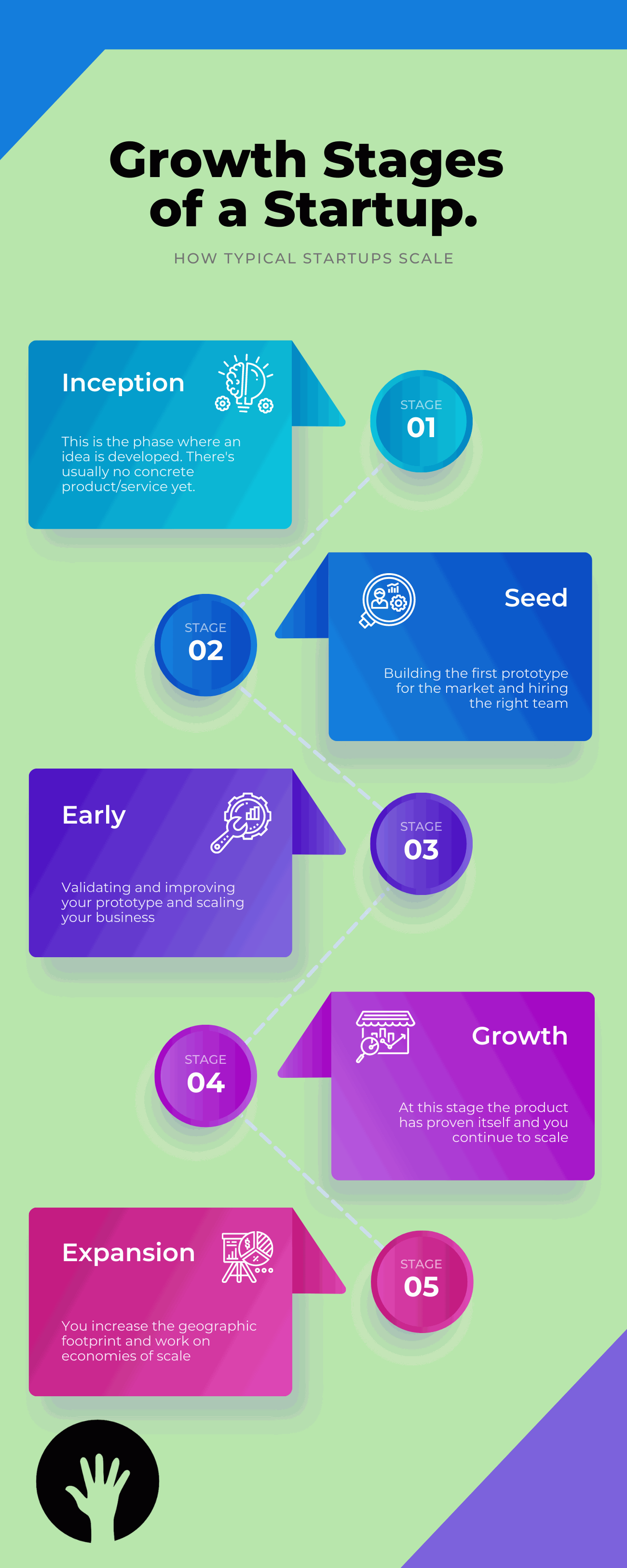
Starting a new business is an exciting and challenging endeavor, and every startup goes through a series of stages as it grows and develops. The four main stage of startup growth are inception, seed, early, and growth.
1. Inception Stage
The inception stage is the very beginning of a startup, where the idea is first conceived. During this stage, the founder(s) identify a problem in the market and come up with a unique solution to address it. This stage is characterized by a lot of research, brainstorming, and idea generation. The goal of the inception stage is to validate the idea and determine whether it has the potential to be a viable business.
The inception stage of a startup is the earliest phase in the journey of creating a new business. During this stage, the founder(s) have identified a problem or opportunity in the market and have come up with an idea for a product or service that can address it. In this, we will explore the key elements of the inception stage and how entrepreneurs can navigate this critical phase of the startup journey.
- Identify a Problem or Opportunity The first step in the inception stage is to identify a problem or opportunity in the market. This could be a gap in the market that is not being addressed or a problem that is not being solved effectively by existing solutions. The key is to find an area where there is a need for a new product or service.
- Conduct Market Research Once a problem or opportunity has been identified, the next step is to conduct market research. This involves gathering information about the market, potential customers, and competitors. Market research can help the founder(s) to validate their idea and determine whether there is a viable market for their product or service.
- Develop a Business Plan Based on market research, the founder(s) can develop a business plan. This should include a description of the product or service, a target market analysis, a marketing plan, and a financial plan. The business plan will serve as a roadmap for the startup, outlining the key steps that need to be taken to bring the product or service to market.
- Create a Prototype or MVP Once the business plan has been developed, the next step is to create a prototype or minimum viable product (MVP). This is a basic version of the product or service that can be used to test the market and gather feedback from potential customers. The MVP should be simple and affordable, allowing the founder(s) to test their idea without investing too much time or money.
- Validate the Idea The final step in the inception stage is to validate the idea. This involves testing the MVP with potential customers and gathering feedback. The goal is to determine whether there is a need for the product or service and whether customers are willing to pay for it. Based on the feedback, the founder(s) can refine the product or service and prepare to move on to the seed stage.
Navigating the inception stage of a startup can be challenging, but there are several key strategies that can help entrepreneurs succeed.
- Focus on the Problem When developing a new product or service, it is easy to become fixated on the solution. However, it is important to remember that the solution is only valuable if it solves a real problem. The key is to focus on the problem and understand the needs of potential customers.
- Conduct Thorough Market Research Market research is critical to the success of a startup, and it is important to conduct thorough research before moving on to the seed stage. This involves gathering information about the market, potential customers, and competitors. The more information the founder(s) have, the better equipped they will be to make informed decisions about the business.
- Build a Strong Network Building a strong network of advisors, mentors, and investors can be invaluable during the inception stage. These individuals can provide guidance, support, and feedback, helping the founder(s) to navigate the challenges of starting a new business.
- Embrace Failure Failure is a natural part of the startup journey, and it is important for the founder(s) to embrace it. By failing fast and learning from mistakes, they can refine their idea and develop a stronger product or service.
In conclusion, the inception stage is a critical phase in the startup journey. It is a time for the founder(s) to identify a problem or opportunity in the market, conduct thorough market research, develop a business plan, and create a prototype or MVP.
2. Seed Stage
Once the idea has been validated, the next step is to start building the business. This is the seed stage, where the founder(s) develop a business plan, create a prototype or minimum viable product (MVP), and begin to test their idea with potential customers. This stage is characterized by a lot of experimentation and iteration, as the founder(s) refine their product or service based on feedback from customers and other stakeholders.
The seed stage is a crucial phase in the life of a startup. This is the stage where the initial investment is made to bring the business idea to life. It is the starting point for any new venture, and it is critical to get it right.
The seed stage is characterized by the development of the business idea and the formation of the founding team. It is a time for experimentation and exploration, where the founders test their hypotheses and refine their vision. The primary goal of this stage is to validate the business idea and determine if it has the potential for success.
One of the main challenges of the seed stage is securing the necessary funding to bring the idea to life. Startups at this stage typically rely on seed funding, which is a type of investment that is typically provided by angel investors or venture capitalists. These investors are looking for promising ideas that have the potential for high growth and profitability.
At this stage, it is also important to develop a clear and compelling business plan. The business plan should outline the product or service that the startup will offer, the target audience, the marketing strategy, and the financial projections for the business. The business plan should be well-researched and include data and statistics that support the viability of the business idea.
Another important aspect of the seed stage is building a strong founding team. The team should consist of individuals with complementary skills and expertise who are passionate about the business idea. The team should be able to work well together, communicate effectively, and be willing to put in the hard work necessary to launch the business.
In addition to developing a strong founding team and a solid business plan, startups at the seed stage should also focus on building a strong brand identity. This includes developing a brand name, logo, and visual identity that resonates with the target audience. The brand should also have a clear mission and vision, as well as core values and a brand personality that reflect the values of the company.
Startups at the seed stage should also focus on building a minimum viable product (MVP). An MVP is a product that has just enough features to satisfy early customers and provide feedback for future product development. The goal of an MVP is to test the viability of the product in the market and make adjustments based on customer feedback.
Finally, startups at the seed stage should focus on building a strong customer base. This can be done through market research, customer surveys, and other forms of customer engagement. The goal should be to understand the needs and desires of the target audience and develop products or services that meet those needs.
In conclusion, the seed stage is a critical phase in the life of a startup. It is the starting point for any new venture, and it is essential to get it right. Startups at this stage should focus on securing the necessary funding, developing a clear and compelling business plan, building a strong founding team, developing a strong brand identity, building a minimum viable product, and building a strong customer base. With these elements in place, startups can position themselves for success in the highly competitive startup landscape.
3. Early Stage
If the startup is successful in the seed stage, it will move on to the early stage. This is where the business begins to scale up and grow, with the founder(s) focusing on customer acquisition, building out their team, and securing additional funding to support growth. During the early stage, the startup will also start to develop its brand and marketing strategy, as it seeks to establish a foothold in the market and differentiate itself from competitors.
The early stage is the next phase in the life of a startup, following the seed stage. At this stage, the startup has received funding and is beginning to grow and scale. This is a critical phase in the life of a startup, as it sets the foundation for future growth and success.
One of the main challenges of the early stage is managing the growth of the business. Startups at this stage need to focus on building a scalable business model that can sustain growth over the long term. This includes developing systems and processes that can handle increased demand, and hiring the right team members to support growth.
Another important aspect of the early stage is refining the product or service. Startups at this stage should focus on improving the MVP and adding features that provide additional value to customers. This can be done through customer feedback, market research, and data analysis.
At the early stage, startups should also focus on building a strong team culture. This includes developing a set of core values that guide the company’s decisions and actions, and creating a work environment that fosters creativity, collaboration, and innovation. The team should also be motivated and aligned with the company’s mission and vision.
Another key aspect of the early stage is building a strong brand identity. This includes developing a strong visual identity, messaging, and positioning that resonates with the target audience. The brand should also have a clear mission and vision, as well as core values and a brand personality that reflect the values of the company.
Marketing and customer acquisition are also critical at the early stage. Startups need to develop a marketing strategy that reaches their target audience and generates leads. This can include a combination of digital marketing, content marketing, social media, and events.
In addition to building a strong customer base, startups at the early stage should also focus on building relationships with strategic partners and investors. Strategic partnerships can help startups reach new customers and expand their reach, while investors can provide additional funding and guidance as the company grows.
Finally, startups at the early stage should focus on building a solid financial foundation. This includes developing financial projections, managing cash flow, and raising additional funding as needed. Startups should also have a clear understanding of their burn rate and runway, and develop contingency plans in case of unexpected challenges.
In conclusion, the early stage is a critical phase in the life of a startup. Startups at this stage need to focus on managing growth, refining the product or service, building a strong team culture, developing a strong brand identity, marketing and customer acquisition, building relationships with strategic partners and investors, and building a solid financial foundation. With these elements in place, startups can position themselves for long-term growth and success in the highly competitive startup landscape.
4. Growth Stage
The growth stage is where the startup starts to see significant growth in terms of revenue, customer acquisition, and market share. At this stage, the founder(s) will focus on expanding their team, increasing production or service capacity, and continuing to refine their product or service to meet the evolving needs of their customers. The goal of the growth stage is to achieve sustained profitability and establish the startup as a major player in its market.
The growth stage is the next phase in the life of a startup, following the early stage. At this stage, the startup has successfully established its product or service in the market and is experiencing rapid growth. This is a crucial phase for a startup, as it must continue to scale and expand its operations while maintaining its position in the market.
One of the main challenges of the growth stage is managing the increased complexity of the business. Startups at this stage must deal with a growing customer base, increased demand for their product or service, and more complex operations. They must focus on building a scalable infrastructure that can handle the increased workload and ensure consistent quality and customer satisfaction.
Another important aspect of the growth stage is expanding the customer base. Startups must continue to refine their marketing strategy and focus on reaching new customers in order to sustain their growth. This can include expanding their marketing efforts, exploring new channels and markets, and developing new products or services that meet the needs of their target audience.
At the growth stage, startups should also focus on developing a strong team culture that can handle the increased demands of the business. This includes hiring new team members and developing a clear career path for existing team members. Startups should also focus on creating a work environment that fosters creativity, collaboration, and innovation, and provides opportunities for personal and professional growth.
Another key aspect of the growth stage is building a strong brand identity that can stand out in a crowded market. Startups must continue to refine their messaging and positioning, and ensure that their brand personality and values resonate with their target audience. This can include developing a strong visual identity, creating engaging content, and building relationships with influencers and industry leaders.
Finance and funding are also critical at the growth stage. Startups must focus on managing cash flow, optimizing their financial operations, and raising additional funding as needed. They must also have a clear understanding of their financial metrics, such as burn rate, churn rate, and customer acquisition cost, in order to make data-driven decisions and ensure long-term sustainability.
In addition to managing growth and expanding the customer base, startups at the growth stage should also focus on building strategic partnerships and relationships with investors. Strategic partnerships can help startups expand their reach and access new markets, while investors can provide additional funding and guidance as the company grows.
Finally, startups at the growth stage must focus on maintaining a strong customer focus and ensuring that their product or service continues to meet the evolving needs of their target audience. This requires ongoing research, testing, and feedback, as well as a commitment to continuous improvement and innovation.
In conclusion, the growth stage is a critical phase in the life of a startup. Startups at this stage must focus on managing growth, expanding the customer base, developing a strong team culture, building a strong brand identity, managing finances and funding, building strategic partnerships and relationships, and maintaining a strong customer focus. With these elements in place, startups can position themselves for long-term growth and success in the highly competitive startup landscape.
