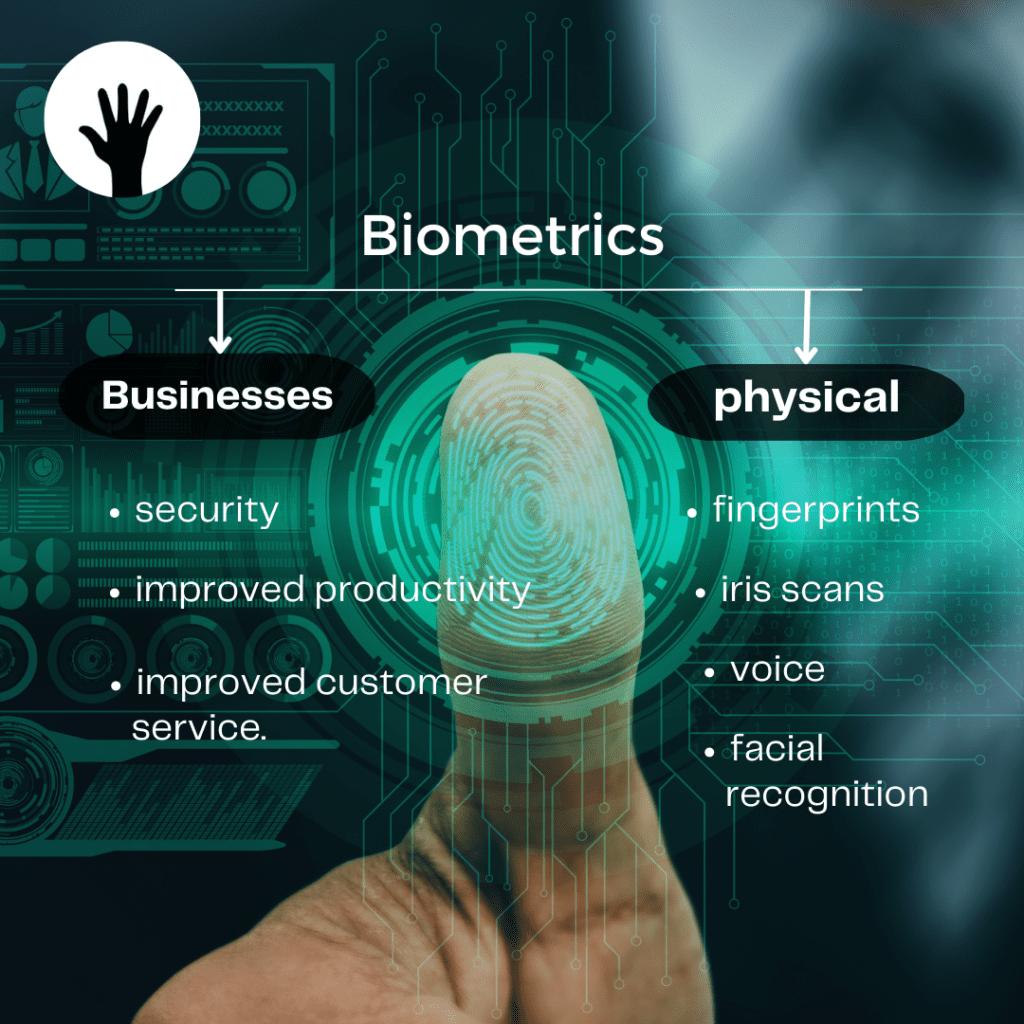
Biometrics is an emerging field of technology that utilizes unique physical identification characteristics to provide quicker and more secure access. It involves using biometric identifiers such as fingerprints, face recognition, voice recognition, and iris scans to identify a person accurately. This reduces the need for passwords and other forms of identification that are vulnerable to theft or loss. Biometrics allows for faster and more secure access to private and confidential information and systems, making it increasingly popular in various industries.
It is an emerging technology field that offers various benefits for both businesses and consumers. These benefits can include enhanced security, improved productivity, and improved customer service. Biometric technologies use physical characteristics such as fingerprints, iris scans, and facial recognition to identify an individual. This technology is becoming increasingly popular due to its ability to provide more precise, accurate, and secure identification than traditional methods.
It is the use of a person’s unique physical characteristics to identify them. This technology is increasingly being used in various contexts, such as home security and authentication. Biometric data can range from something as simple as a fingerprint to more complex methods such as facial recognition. It is even possible to use a person’s voice to identify them.
The use of physical characteristics such as fingerprints, facial recognition, and voice patterns to identify individuals, has become increasingly popular in the past few years. This technology can be used to verify identity, grant or deny access, or provide added security for systems. Biometrics offers several advantages over traditional methods of identification, such as improved accuracy and ease of use. Additionally, biometric data can be collected remotely, making it accessible for a variety of applications.
This is a rapidly advancing field of technology that integrates human physiology and behavior into security measures. Biometric authentication methods measure and analyze an individual’s physical characteristics, such as voice, fingerprint, face, or iris recognition, to grant or deny access to computer systems and networks. Recent advancements have enabled these authentication systems to be more accurate, reliable, and user-friendly, leaving the traditional security measures of passwords and pins increasingly obsolete. Biometric authentication systems are becoming more widely adopted among many organizations due to their ability to provide enhanced security.
These authentication systems are becoming increasingly popular due to their capacity to provide a higher level of security. Unlike traditional methods of authentication, biometrics use unique physical characteristics that cannot be replicated or easily stolen, making it difficult for unauthorized personnel to access confidential information. Furthermore, biometrics can be used to identify an individual more accurately than traditional methods, eliminating the potential for human error in the authentication process. Additionally, since biometric data is collected remotely, it is convenient and cost-effective for organizations to utilize.
This is also becoming more cost-effective. As more organizations turn to biometric authentication methods, the cost of these systems is decreasing due to increased competition in the market. Additionally, these systems can perform multiple tasks simultaneously, thus reducing labor costs. Furthermore, biometric authentication technology is sophisticated enough to prevent unauthorized individuals from accessing sensitive data or facilities.
This technology has many potential applications, ranging from physical access control to automated financial transactions. In addition to providing increased security, biometric authentication systems can also be used for identity management, authentication for online applications, and authentication for mobile devices. This technology can also be used to improve customer experience and reduce fraud, as it increases accuracy, reduces costs associated with manual authentication, and improves user convenience. Furthermore, biometric authentication can be integrated with existing systems, making it easy to implement and cost-effective.
Despite the increased security that biometric authentication systems provide, there are still certain drawbacks associated with them. Privacy is one of the most notable issues, as biometric data is often stored in a central database and can be accessed by a variety of people. In addition, biometric data can be difficult and costly to update, as many biometric sensors cannot detect simple changes in physical characteristics. Finally, biometric authentication systems are vulnerable to spoofing, where a person can use a fake biometric sample to gain access to the system.
This has also enabled a safer and more secure environment in the physical world, such as in airports and government buildings. By integrating biometrics into their security systems, access to these facilities can be more accurately monitored, providing an added layer of security. Additionally, biometric authentication systems can be used for identity verification in a variety of different settings such as online banking, electronic payments, and logins to various websites. These services are often more secure and convenient, as they eliminate the need for passwords and pins that can be easily forgotten or stolen.
This can also provide an added layer of security when it comes to protecting sensitive data. By storing biometric data in a secure database, access to that data can be tightly regulated and monitored. Furthermore, biometrics can offer greater levels of data privacy, as biometric data is more difficult to replicate than other forms of authentication, such as passwords. As the use of biometrics becomes more widespread, the need for secure methods of authentication will increase, and biometrics will be a valuable tool in providing this security.
Despite the numerous benefits of biometrics, there are some drawbacks to consider. For instance, biometric information can be easily stolen or breached if not properly secured. Furthermore, the data collected by biometrics are typically stored. Additionally, the accuracy of biometric authentication systems is often dependent on the quality of the data and the type of sensors used. Therefore, it is important to ensure that the data is collected and stored securely.
In addition to providing added security, biometrics can be used to collect and analyze data that can be used to improve products and services. This data can be used to identify patterns of behavior, such as how customers interact with a product or service, which can be used for marketing and research purposes. Additionally, biometrics can be used to monitor employee productivity and to track the usage of certain resources. With this data, companies can make better decisions about the allocation of resources, providing an overall improved experience for their customers.
Biometrics can also be used to increase convenience in everyday life. Services such as Apple’s Touch ID provide an easy and secure way to unlock iPhones and iPads, and various companies are now providing biometric payment systems that provide an alternative to traditional credit card payments. With biometrics, users can quickly and easily access their devices and services without having to remember long passwords or PINs. As a result, biometrics are becoming increasingly popular as an authentication method, providing greater convenience and security for today’s digital world.
Biometrics authentication has the potential to increase security and convenience in many areas. As biometrics become more widespread, the technology will become more reliable and less expensive. With proper implementation and security protocols, biometric authentication systems can be an effective way to protect sensitive data and personal information. In addition, biometrics can provide a more user-friendly experience, as it eliminates the need for remembering long passwords and pins.
This authentication can also improve the usability of products and services. For example, a device with biometric authentication can be quickly unlocked with a single touch or glance, allowing the user to quickly access content and services without having to remember complex passwords. Additionally, biometric authentication solutions can be integrated into existing authentication systems, providing an additional layer of security that is both user-friendly and secure. Moreover, biometrics can provide an additional level of authentication for online services that require extra security, such as banking and payment services.
Biometrics is also beneficial in many other contexts. For example, biometric authentication can be used to access banking and financial information, as well as other sensitive personal information such as health records. Biometrics can also be used to verify identity, making it difficult for unauthorized individuals to access someone’s data. In addition, biometrics can help to reduce fraud and provide greater security for online transactions.
Biometric authentication is not without its limitations, however. It can be difficult to implement in some environments, and there are privacy and security concerns. Additionally, false positives and false negatives can be an issue, as biometric authentication relies upon the accuracy of the algorithms used to capture and analyze biometric data. Finally, biometric data itself can be vulnerable to compromise, as it is one of the few types of data that cannot be changed.
They are not just limited to unlocking devices and making payments. In healthcare, biometric technology can be used to help secure patient records and other sensitive data. In the banking industry, biometrics can help to verify customer identity and ensure that transactions are being made securely. Furthermore, biometrics can be used in government applications, such as passport and immigration control, to help verify citizens’ identities.
This can also be used as an additional layer of security in conjunction with traditional authentication methods such as usernames and passwords. For instance, a bank may require a user to input their password and then use biometrics to further verify their identity. This ensures that only authorized users have access to the sensitive information, helping to protect both the user and the business from potential fraud and data breaches. Additionally, biometric authentication systems can help reduce the cost associated with manual authentication processes.
